Google uses over 200 ranking factors in their algorithm – did you know that? Content might steal the spotlight, but technical SEO is the hidden architect of your website’s search performance that silently shapes your success or failure in search results. Technical SEO involves optimisations that improve your website’s infrastructure. This helps search engines to crawl, index and rank your pages effectively. Search engines review elements like site speed, mobile-friendliness and crawlability to determine your position in search results. These are the foundations of strong search performance.
Your website needs more than just a well-optimised technical foundation to please search engines. A strong technical base substantially improves your website’s performance and security. It can boost conversion rates through specific factors. Your beautiful website will eventually collapse if you ignore these technical elements – just like a house built on weak foundations. Site speed stands out as a vital technical SEO ranking factor. Your search rankings can take a serious hit from slow-loading websites that frustrate visitors. A technically sound website needs proper site architecture, clean URL structure and secure HTTPS connections. These elements help users and search engines to traverse your site smoothly.
This piece reveals why technical SEO remains key to top Google rankings. You’ll find the most influential technical factors that affect your visibility. We’ll also cover practical steps to build your website’s technical foundation for better search performance.

What Is Technical SEO and Why It Still Matters
Technical SEO is the vital framework that builds successful search visibility. Your website stays invisible to search engines without this foundation, no matter how good your content is. The technical side of optimisation bridges the gap between your website and search engine crawlers. This determines if your pages show up in searches.
Definition of technical SEO in modern search
Technical SEO is about optimising your website’s infrastructure so search engines can crawl, render, index, and show your content properly. It fine-tunes a website’s technical elements to boost its performance in search engine rankings. Your content needs technical SEO as its base to show up in searches.
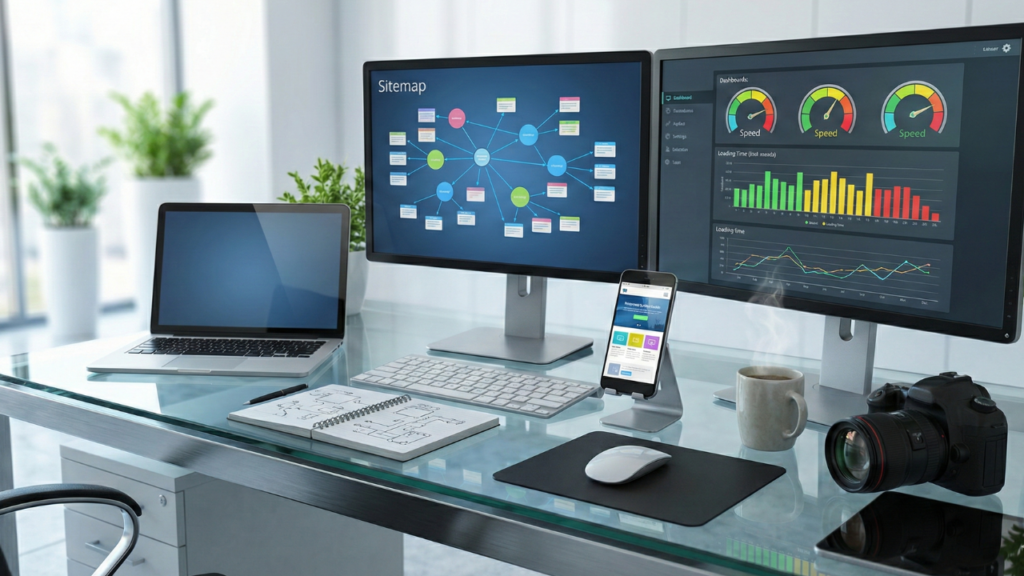
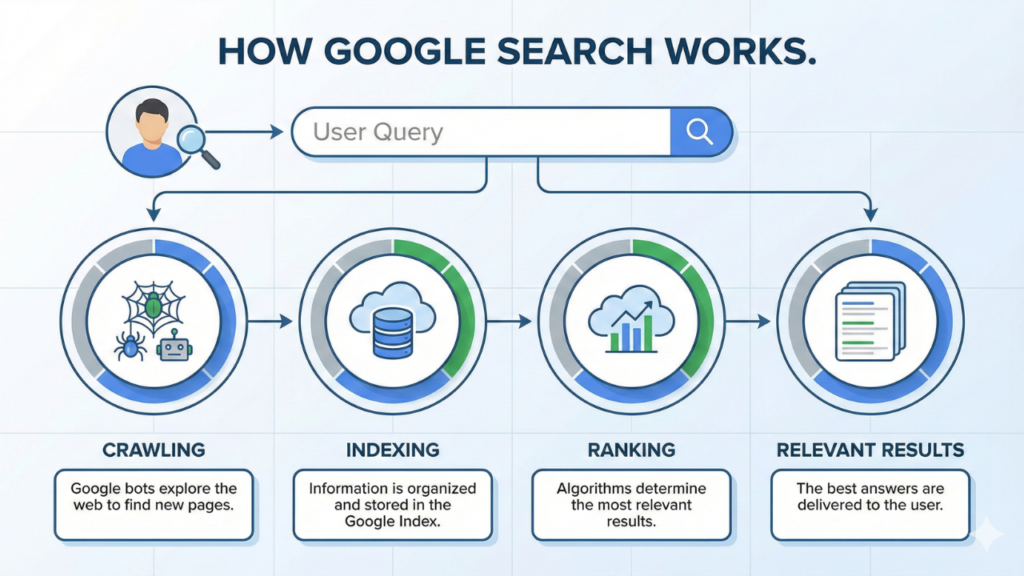
Google sees your site through these vital steps:
- Crawling: Can search engine bots reach your pages through internal links and sitemap instructions?
- Rendering: Can Google load your content fully, including JavaScript, images, and dynamic elements?
- Indexing: Does your website’s structure let search engines store and organise your content in their database?
- Ranking: Does your site’s technical setup help or limit your chances to appear in search results?
Technical SEO lets you control these vital steps and manage how search engines work with your website. The best content won’t reach anyone without proper technical setup, just like luxury trains need well-built tracks to run. Technical SEO matters because it affects how your website performs in Google’s search results. Search engines won’t show or rank your web pages well if they can’t access and understand them. This leads to lost visitors and revenue. The technical foundation supports three main parts: search engine visibility, website performance, and structured data setup. Good technical optimisation verifies your website’s server settings, resource management, and structured data to help search engine efficiency.
How it is different from on-page and off-page SEO
Technical SEO plays a unique role compared to other SEO types. It focuses on your website’s structure and architecture to help search engines crawl and index it well. On-page SEO works on content optimisation and relevant keywords. Technical SEO puts performance first, while on-page SEO focuses on content. They work as a team, technical SEO ensures visibility while on-page SEO delivers relevance. Off-page SEO builds trust through backlinks and other external factors you don’t control directly.
These elements work like pillars of a well-built website. You need all three to succeed, but technical SEO controls whether people see your content at all. Big publishers often spend heavily on great content but don’t deal very well with their technical foundation. This limits how visible they can be. The core team looks at specific elements. Technical SEO includes site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexation, XML sitemaps, and security protocols. On-page SEO works with content quality, keyword optimisation, and meta descriptions to boost relevance. Off-page SEO builds authority through backlinks, social signals, and other external factors.
Technical optimisation provides the structure that supports both on-page and off-page work. Even the best content and strongest backlinks can’t realise their full ranking potential without this solid base. Start with technical SEO before anything else—fix the foundation first, then build on it. Don’t see these as competing priorities. Think of them as parts of one integrated approach. A technically sound website with good content and strong external signals creates perfect conditions to succeed in search.
How Technical SEO Supports Google’s Ranking Algorithm
Google’s search algorithm depends on technical foundations before it looks at content quality or backlink authority. Your website becomes invisible to search engines without proper technical SEO – no matter how good your content might be.
How Technical SEO Supports Google’s Ranking Algorithm
Technical SEO builds the infrastructure that lets Google’s complex ranking system assess your pages properly. The connection between technical elements and ranking power works both directly and indirectly. This forms the base that other ranking signals need.
Crawlability and indexation as ranking prerequisites
Google must first find, crawl, and index your content before your website can rank for any search query. These steps must happen first, your pages won’t show up in search results without them, whatever their quality or relevance. Crawlability means Google knows how to access and direct through your website. Think of Google’s crawlers as explorers mapping your digital territory, they need clear paths to follow. Large parts of your website stay hidden when technical barriers block these paths. Common issues include JavaScript rendering problems, broken internal links, and wrong robots.txt directives that block important content by mistake.
Your content needs proper indexing after being crawled – it must be added to Google’s massive database of web pages. Technical SEO tells Google which content should be indexed and which should stay out. Google might skip your best pages or waste time on duplicate or low-quality content without proper guidance.
These technical factors make crawling and indexing work:
- Robots.txt configuration: Shows search engines which parts of your site to access or avoid
- XML sitemaps: Makes a roadmap of your important pages so crawling works better
- URL parameters handling: Stops crawlers from getting stuck in infinite loops
- Canonical tags: Points to which version of similar content should be indexed
- Internal linking structure: Makes paths for crawlers to find all your content
These technical elements open the door to ranking potential. Small technical errors can create big barriers that stop great content from competing in search results.
Impact of site structure on search engine understanding
Site structure does more than organise, it shapes how search engines understand your content’s meaning and connections. A well-laid-out website shows clear information hierarchies that help Google figure out what topics matter and where you have authority. Your website’s architecture tells Google what’s important and how things connect. Pages closer to the root domain get more “link equity” and seem more important. Content grouped in logical categories helps search engines see topical connections – this matters more as Google focuses on topic authority instead of just matching keywords. Internal linking patterns help Google understand your content. These links create paths for crawlers and context. Smart internal linking helps search engines:
- See how content pieces connect
- Find your most important pages
- Know your main topics and subtopics
- Share ranking power across your site
Clear URL structure helps search engines understand better. URLs with logical folder hierarchies give more context about content relationships and importance. This organised approach lets Google put your content in the right topical areas. Technical SEO creates a framework that supports meaning. Google’s algorithm has moved from matching keywords to understanding user intent. It needs structured data, content relationships, and technical signals to know what your content means. A technically sound website gives Google the clarity it needs to match your content with relevant searches – that’s what makes ranking work. Building solid technical infrastructure creates the right conditions for Google to assess your content’s quality, relevance, and authority. These factors determine where you end up in search results.
Top 8 Technical SEO Factors That Influence Rankings
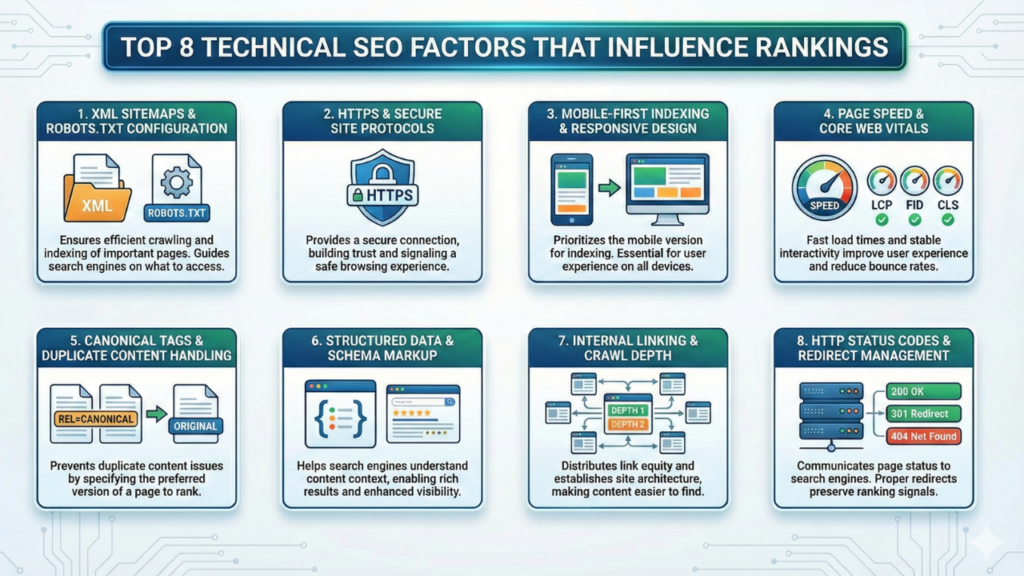
Eight key ranking factors make or break your website’s visibility in search results. A solid foundation comes from getting these elements right. Poor technical implementation can hold back even the best content from ranking well.
1. XML sitemaps and robots.txt configuration
XML sitemaps work as your website’s roadmap and show search engines your important pages. These files list all pages you want indexed, which helps Google crawl more quickly. Your robots.txt file tells search engines which sections they should crawl or skip. Both elements help search engines use their resources better during crawling. The best setup puts your XML sitemap at your domain’s root and lists it in robots.txt like this: Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml. Google will find your sitemap automatically during crawling with this simple step.
2. HTTPS and secure site protocols
Modern technical SEO demands security. Google has used HTTPS as a ranking signal since 2014. HTTPS sites rank better and load faster because their security checks run more smoothly than HTTP. Users see “Not Secure” warnings on non-HTTPS sites in Chrome and other browsers. This warning changes how people behave on your site, which can tank your traffic and search rankings.
3. Mobile-first indexing and responsive design
Your site’s mobile version now determines how Google indexes and ranks your content. This approach means mobile experience directly affects your search visibility. Responsive design offers the best solution for mobile SEO. It uses one flexible codebase that fits any screen size. Google expects identical content on mobile and desktop versions. Better mobile experiences lead to higher search rankings, giving websites a competitive edge.
4. Page speed and Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals measure real-life user experience through loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. These metrics affect your search position. Good performance requires: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Under 2.5 seconds Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Under 200 milliseconds Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Under 0.1. Google looks at the 75th percentile of actual user experiences over 28 days to calculate these metrics.
5. Canonical tags and duplicate content handling
Search engines rely on canonical tags to know which version of similar content they should index. This tool combines signals from duplicate pages and directs link equity to your preferred URL. Adding canonical tags requires a simple step – insert <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/preferred-page” /> in your page’s HTML head section. This helps avoid duplicate content issues and shows search engines your authoritative URL.
6. Structured data and schema markup
Structured data gives Google clear signals about your content’s meaning through standard formats. Search engines understand your content better and can show rich results that get more clicks. Results speak for themselves – Rotten Tomatoes saw 25% more clicks on pages with structured data. Food Network’s visits jumped 35% after adding structured data. Google accepts several structured data formats, though JSON-LD works best.
7. Internal linking and crawl depth
Internal links create paths through your site that help users and search engines. Each link adds context through its anchor text – the words users click. Pages become harder to index as crawl depth increases. Keep important pages within three clicks of your homepage for the best results. Search engines can find and index key content quickly this way, and important pages stay close to the surface of your site structure.
8. HTTP status codes and redirect management
HTTP status codes tell search engines about your pages’ condition. Using the right status codes prevents indexing problems and saves ranking signals. Moving content permanently needs 301 redirects to pass link equity to new URLs. Removed content should return 404 (not found) or 410 (gone) status codes to clearly tell search engines the page no longer exists. Watch for and fix 5XX server errors quickly – they hurt crawling and can lead to pages dropping from the index.
Why Page Speed and Core Web Vitals Are Non-Negotiable
Core Web Vitals have become vital ranking factors that directly affect your search visibility. These performance metrics measure real-life user experience and set clear thresholds to determine your site’s performance. Your technical SEO success now depends on understanding and optimising these metrics.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) thresholds
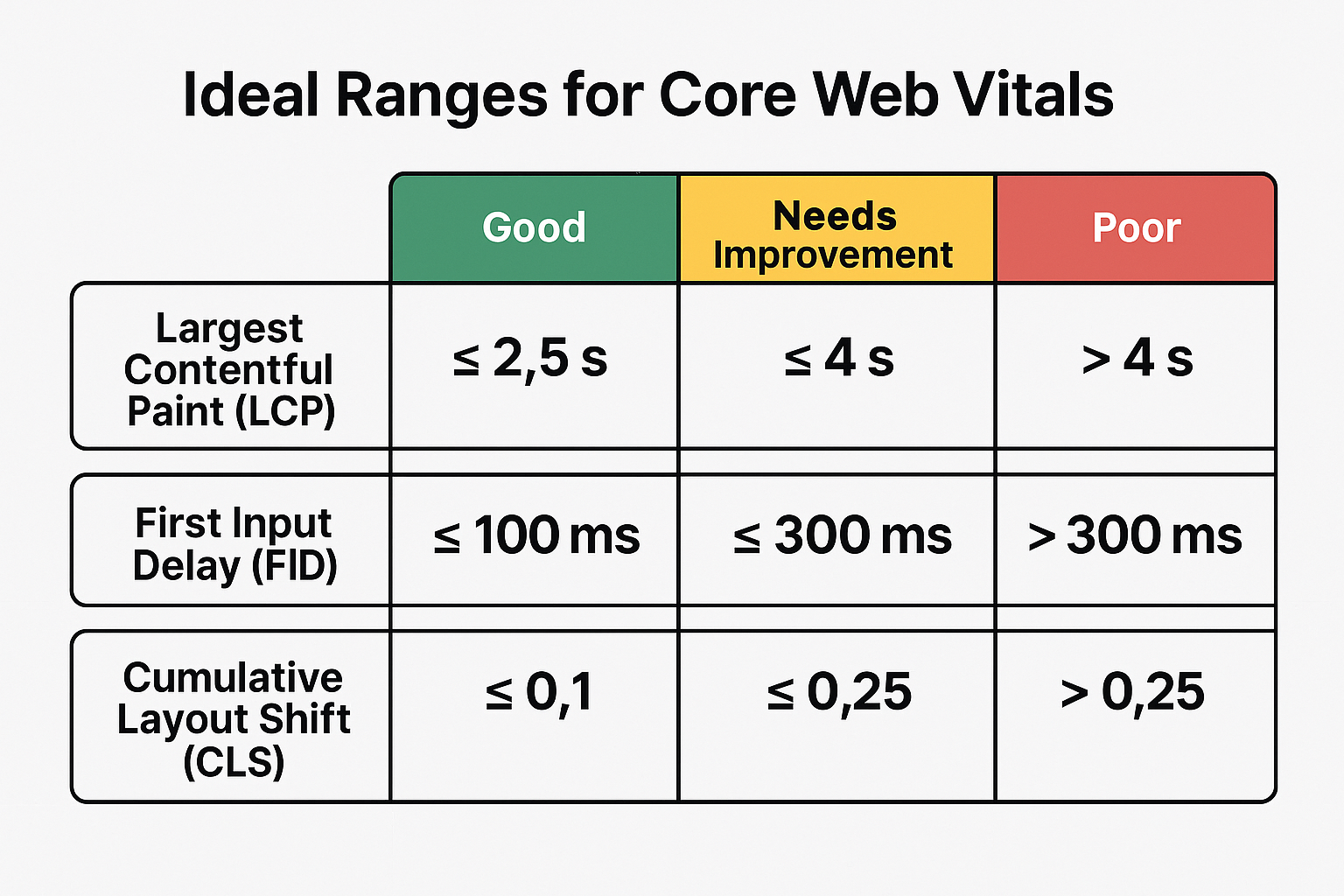
LCP measures how fast the largest content element in the viewport appears on screen. This metric tells us when users can see your main content, making it a key signal for user experience. Your pages must load their largest elements within 2.5 seconds to get a “good” rating. Pages loading between 2.5-4.0 seconds need work, while anything over 4 seconds is poor. Google looks at real user experiences rather than lab tests and uses the 75th percentile of page loads over 28 days. LCP timing has four parts: Time to First Byte (server response), Load delay (time between TTFB and resource loading start), Load time (duration to load the resource), and Render delay (time until final rendering). Better rankings come from optimising each of these components to achieve faster LCP scores.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) and visual stability
Visual stability makes a big difference in user experience. Unexpected movements frustrate visitors and can lead to wrong clicks. CLS measures these unwanted shifts throughout the page’s lifecycle. A CLS score below 0.1 will give users the best experience. This number means your page stays stable while loading. Higher scores point to layout shifts that annoy users and hurt conversion rates.
Two factors determine CLS: impact fraction (shifted visible content) and distance fraction (element movement distance). The final score shows the biggest burst of layout shifts happening quickly, with each session window lasting 5 seconds. Bad CLS scores often come from images without dimensions, dynamic content, ads, animations, and web fonts rendering differently than their fallbacks. Site stability improves dramatically by saving space for dynamic elements and sizing media correctly.
First Input Delay (FID) and interactivity
FID shows how responsive your site is by tracking delays between user interactions and browser responses. This metric tells you how fast your site reacts when someone tries to use it. FID started as a Core Web Vital with a 100 millisecond threshold. Google has replaced it with Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which needs 200 milliseconds. This change helps measure responsiveness throughout the user’s entire experience instead of just the first interaction.
Both metrics show how heavy JavaScript and main thread blocking can create delays that frustrate users. Sites score poorly when they run too much JavaScript during page load or let third-party scripts block the main thread. Technical SEO now demands more than fast loading times. Your search rankings depend just as much on how well your site responds to users and stays visually stable.
The Role of Structured Data in Enhancing Visibility
Structured data acts as a bridge between your website and search engines. It makes your content stand out in search results. This standardised format helps search engines understand your content’s meaning, not just its words. Well-implemented structured data goes way beyond the reach and influence of simple SEO by creating rich results that grab attention and boost engagement.
Schema.org markup for rich results
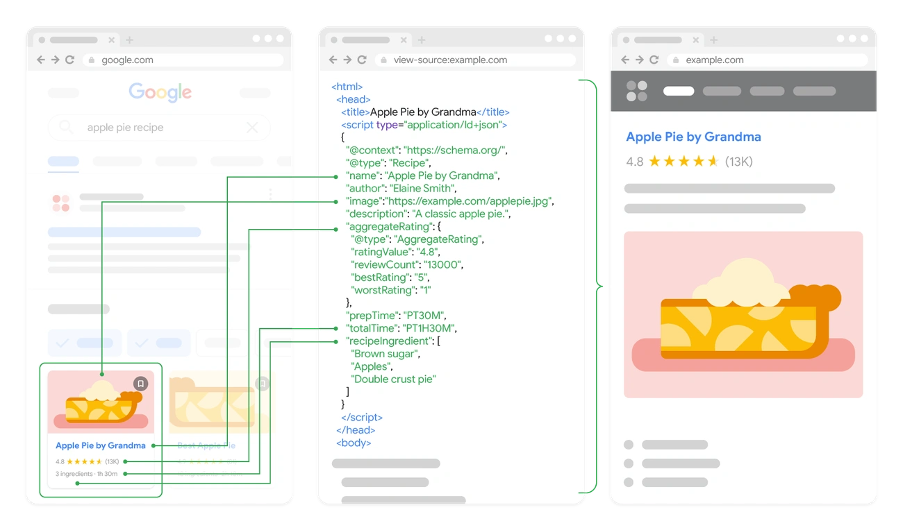
Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex worked together to create Schema.org as a universal vocabulary for structured data. Their shared language helps search engines display your content better. Schema markup can reshape the scene of ordinary search listings into eye-catching rich results with star ratings, FAQ dropdowns, and featured snippets.
The numbers prove Schema markup’s value. Websites using structured data show impressive visibility gains. Rotten Tomatoes saw a 25% higher click-through rate on pages that used structured data compared to regular ones. Food Network turned 80% of their pages into search-friendly versions and saw visits jump by 35%. These improvements happened even though structured data isn’t a direct ranking factor.
JSON-LD vs Microdata implementation
You have two main choices for adding structured data: JSON-LD and Microdata. Google prefers JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data). This format keeps structured data separate from visible content in a dedicated script tag, making it easier to manage with fewer errors.
Microdata takes a different approach by embedding structured data right into HTML elements. This creates a closer link between content and markup but needs more upkeep and could cause problems during site updates. It gives you detailed control through HTML tags but might complicate future changes. JSON-LD’s benefits explain why Google likes it so much. It separates markup from content, makes implementation simpler, and helps fix problems faster. JSON-LD also works great with JavaScript-heavy websites and dynamic content where Microdata might struggle.
Testing with Google’s Rich Results Tool
Testing becomes vital after you add structured data to ensure search engines read your markup correctly. Google’s Rich Results Test helps validate your pages for enhanced search features. The tool lets you test by URL or direct code input. You can check results for both smartphone and desktop crawlers, though mobile comes first in today’s world. Test results show which rich features you qualify for, preview search appearances, and point out any issues. Fix red errors right away since they block rich results eligibility. Orange warnings suggest areas for improvement. A passing test means you could get rich results, but Google still decides when to show enhanced listings based on many factors.
Technical SEO Tools That Power High Rankings
You just need powerful tools to identify opportunities and find hidden issues that affect your rankings. Professional SEO practitioners use specialised software to analyse, diagnose, and optimise websites for better search visibility.
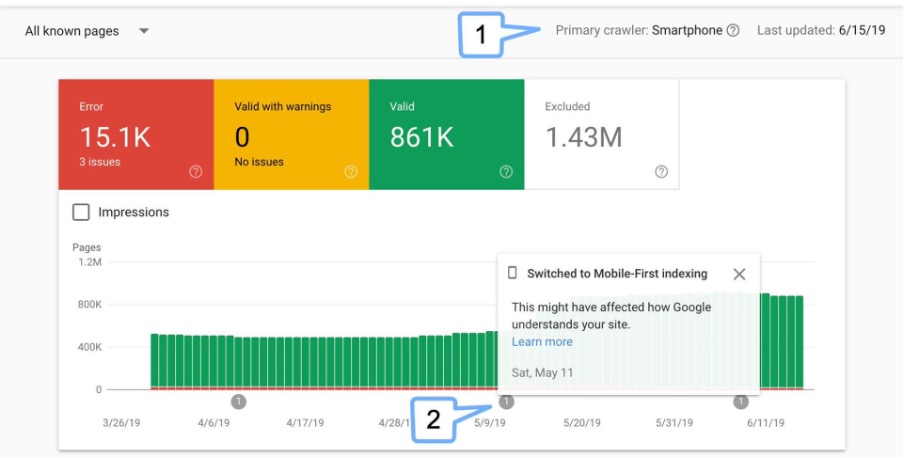
Google Search Console for crawl and index insights
Google Search Console (GSC) is a vital source of truth to learn about how Google sees your website. This free tool gives direct feedback from Google and is a great way to get technical SEO implementation right. GSC shows which pages are indexed, tracks performance metrics, and alerts you to significant issues that could affect your visibility in search results.
The Index Coverage report shows exactly which pages Google can and cannot index, along with specific reasons for exclusion such as crawl errors or noindex tags. This helps you quickly fix indexation barriers that stop your content from ranking. GSC lets you monitor crawl stats and shows how often Google visits your site and which resources it downloads. This information is vital to manage crawl budget on larger websites.
PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse for performance
PageSpeed Insights combines laboratory testing with ground data to provide complete performance analysis. The tool uses Lighthouse as its analysis engine to simulate mobile device loading and compute key performance metrics. Each analysed page gets a performance score from 0-100, and scores above 90 are good.
Lighthouse comes built right into Chrome and lets you run technical health checks with just a few clicks. The tool assesses accessibility, SEO fundamentals, and adherence to web development best practises. This versatility helps identify technical issues that affect both user experience and search rankings. Chrome DevTools integration lets developers diagnose and fix performance bottlenecks without installing additional software.
Screaming Frog and Sitebulb for audits
Screaming Frog SEO Spider is the industry standard tool for complete technical audits. This desktop crawler scans entire websites and finds issues like broken links, redirect chains, missing meta tags, and duplicate content. Its strength lies in knowing how to crawl sites of any size while giving you full control over the collected data.
Sitebulb offers advanced crawling capabilities with user-friendly reporting especially when you have to create visual insights. The tool excels at showing complex technical data in digestible formats, which makes it exceptional for client deliverables. Both tools support JavaScript rendering and XML sitemap generation, which are vital capabilities when working with modern web applications or large ecommerce platforms. These specialised auditing tools help you find and fix technical barriers that stop your website from reaching top rankings.
Conducting a Technical SEO Audit: Step-by-Step
Your site might not reach its full ranking potential due to technical SEO issues that a thorough audit can uncover. You should run regular audits to keep your technical SEO healthy and spot problems before they hurt your rankings.
Crawl the site and identify errors
A dedicated crawler like Screaming Frog SEO Spider should scan your entire website. This tool finds broken links, server errors and redirect chains. It automatically spots common SEO problems such as duplicate content, missing meta tags and canonical issues. You need to pay special attention to client errors (4XX) and server errors (5XX) since they block proper indexation. Developers can quickly fix these issues thanks to Screaming Frog’s bulk export feature.
Check indexation and canonicalisation
Search engines must properly index your pages. Your robots.txt file should not accidentally block important content. The XML sitemap must list all relevant URLs but exclude non-canonical pages. Google’s Search Console helps you see which pages Google treats as canonical. Remember that Google might pick different pages than your explicit canonical tags based on content quality. Look for non-indexable canonical issues where canonical URLs lead to blocked, redirected or error pages.
Test structured data and mobile usability
Google’s Rich Results Test shows if your structured data qualifies for enhanced search features. Mobile usability needs testing with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test, since 88% of users think about leaving after just one poor experience. The navigation flow, functionality, responsiveness and accessibility should work well on all devices and screen sizes.
Common Technical SEO Mistakes That Hurt Rankings
Technical SEO mistakes can silently damage rankings, even for seasoned webmasters. These errors often lurk undetected for months and slowly eat away at your search visibility without clear warning signs.
Blocking important pages in robots.txt
Your visibility can take a massive hit from robots.txt configuration errors. Many sites block crucial content by accident, which stops Google from crawling pages meant to rank. Without doubt, you’ll cause the most damage by blocking URLs that have canonical tags or hreflang annotations – search engines can’t see these directives if they can’t access the page. This typically happens as sites try to manage crawl budget by limiting access to faceted navigation or filtered product pages.
Incorrect canonical tags
Poor canonical implementation splits your ranking signals apart. Search engines get confused about which version to index when pages have multiple canonical tags. On top of that, it creates unnecessary complexity to point canonical tags at redirecting URLs, which can weaken ranking power. We noticed this most often with ecommerce sites where category pages exist under different URL structures, creating confusion about the version that should rank.
Unoptimised mobile layouts
Google’s mobile-first indexing means poor mobile experiences now directly hurt your rankings. Content missing from your mobile version might as well not exist for ranking. Many websites still show less content on mobile or make things worse by blocking mobile versions in robots.txt. Rich results won’t show up if mobile pages lack structured data, whatever your desktop version looks like.
Conclusion
Technical SEO stands as the foundation for successful search visibility. This article explains why technical optimisation drives most top Google rankings. Your website can’t compete effectively without solid technical foundations, no matter how great your content is. Google’s algorithm starts by evaluating your site’s technical infrastructure before looking at content quality or backlink authority. You need to master eight critical technical factors – from proper XML sitemap configuration to HTTP status codes. These create competitive advantages that other SEO efforts can’t overcome.
Core Web Vitals need your immediate attention as non-negotiable ranking factors. These performance metrics measure real-life user experiences through LCP, CLS, and interactivity scores. Sites that fall short of these thresholds face major visibility limits. Those exceeding expectations see ranking benefits across their content. Structured data plays a key role in boosting search visibility. While it’s not a direct ranking factor, proper schema markup boosts click-through rates through rich results. The data proves it – websites with structured data perform better than those without it.
Mobile optimisation has become essential since Google adopted mobile-first indexing. Your mobile experience determines your search rankings directly. Responsive design isn’t optional anymore if you want competitive visibility. Note that content missing from your mobile version doesn’t exist for ranking purposes. Regular technical audits with tools like Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Screaming Frog help catch critical issues early. These systematic checks reveal hidden problems that stop your site from reaching its ranking potential.
Technical SEO problems can hide undetected for months and silently hurt your search visibility. Wrong canonical tags, accidental robots.txt blocks, and poor mobile experiences damage your ranking potential through these hidden issues. Technical SEO works alongside content and link building – they’re not competing priorities. A technically sound website makes your content strategy more effective and strengthens your backlink profile.
Technical SEO needs consistent attention and investment. The returns show up as higher rankings, better visibility, and improved user experiences that bring more qualified traffic to your business. Even the best content becomes worthless if search engines can’t crawl, render, index and rank it properly. Your commitment to technical excellence builds the foundation needed for lasting search success. Algorithm updates and trends will keep changing, but technical SEO’s importance stays constant – driving 80% of top Google rankings today and into the future.
Key Takeaways
Technical SEO forms the invisible foundation that determines whether your content can compete in search results, regardless of quality or relevance.
- Technical SEO drives 80% of top rankings – Google evaluates your site’s infrastructure before considering content quality or backlinks.
- Core Web Vitals are non-negotiable ranking factors – LCP under 2.5 seconds, CLS below 0.1, and INP under 200ms directly impact visibility.
- Mobile-first indexing makes responsive design mandatory – Your mobile experience now determines desktop rankings under Google’s current approach.
- Structured data boosts click-through rates by 25% – Schema markup enables rich results that dramatically increase search visibility and engagement.
- Regular technical audits prevent silent ranking erosion – Hidden issues like robots.txt blocks and canonical errors can damage visibility for months undetected
Technical SEO isn’t competing with content strategy, it’s the foundation that amplifies everything else. Without proper crawlability, site speed, and mobile optimisation, even exceptional content remains invisible to search engines. Focus on technical excellence first, then build your content and link strategies upon this solid foundation for sustainable search success.
FAQs
Q1. How does technical SEO influence search engine rankings? Technical SEO plays a crucial role in improving a website’s visibility in search results. It optimises the site structure and infrastructure, making it easier for search engines to crawl, index, and understand the content. Without a solid technical foundation, even high-quality content may struggle to achieve top rankings.
Q2. Why is technical SEO considered essential for website performance? Technical SEO is vital because it addresses fundamental issues that can impact a site’s search visibility and user experience. It ensures proper indexation, improves site speed, enhances mobile responsiveness, and helps search engines interpret content correctly. These factors directly influence how well a website performs in search results.
Q3. Can a website rank well on Google without SEO? While it’s possible for a website to rank for certain queries without deliberate SEO efforts, implementing SEO best practises significantly increases the chances of achieving and maintaining high rankings. SEO helps websites appear more prominently in search results, driving organic traffic and improving overall visibility.
Q4. What are the primary objectives of technical SEO? The main goals of technical SEO are to improve website crawlability, ensure proper indexation, enhance site speed and performance, optimise for mobile devices, and implement structured data. These objectives work together to create a strong technical foundation that supports better search engine rankings and user experience.
Q5. How does mobile optimisation affect search rankings? Mobile optimisation is critical for search rankings due to Google’s mobile-first indexing approach. This means Google primarily uses the mobile version of a site for indexing and ranking. Websites that are not mobile-friendly or have less content on mobile versions may see negative impacts on their search visibility across both mobile and desktop results.
